
A computer memory is an integral part of every central processing unit in computers. It allows proper functioning of computer applications and it also provides easy access of files stored in your drive. Different types of memory hardware are designed to keep files secure in your computer even without continuous supply of power. It is the reason that you can still view files stored in your compute even after you have shut your unit down, exactly in the same state as you saved it previously.
Computer memory is generally subdivided into two categories: internal memory and external memory. The first type allows faster access of information needed by computer programs to function properly and seamlessly. External memory, on the other hand, are units that are larger in capacity, allowing users to store large files and access them on demand. External memory is usually referred to as storage, whereas internal memory is simply called memory.
You may check out this article to know the differences between memory vs storage and learn which specifications are best for your unit. Meanwhile, here are the four types of computer memory that you should know.
External Memory

External memory or storage is, perhaps, the type of memory that most of us are already familiar with. This is where your files are saved, stored, and retained for future access. It is also called secondary memory owing to the fact that your unit may still function correctly even if these files are removed from your system. It can be embedded in your unit as hard disk drives or solid state drives and it can also be in the form of removable devices such as compact disks, external drives, and flash drives.
Read Only Memory
Read Only Memory, also known as ROM, is a type of permanent memory containing small amounts of data that can be accessed anytime within the system. As its name suggests, the information stored in the hardware can never be removed nor overwritten. It is also a non-volatile memory device which keeps the stored information intact even without power source. The ROM contains important operating system data that are accessed immediately during boot.
Random Access Memory
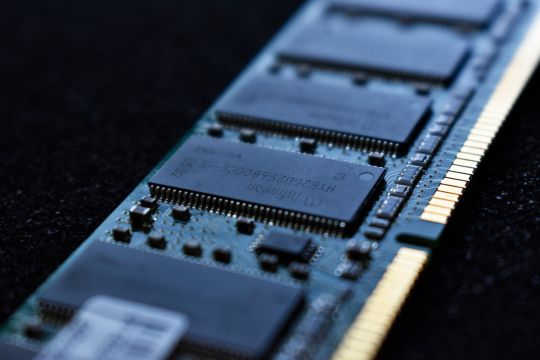
In contrast to ROM, the data stored in Random Access Memory or RAM is volatile. It means that information kept in the hardware will no longer be retained once power is cut off. This is where small chunks of data are kept temporarily to speed up the processing time. It allows programs to access and read information faster without the need to scan high volume of data stored in external storages. The more RAM your computer has, the more capable it is in executing multiple tasks without lag time.
Cache Memory
![]()
Cache memory works the same way as RAM but instead of using the main memory, it comprises smaller bits of data that allow faster loading times in applications. It can act as both temporary and permanent storage device that can be used by applications to load faster and avoid loss of important data too.
